Imagine you wake up one morning to a bizarre change: all the salt in all the oceans has suddenly vanished. For the first 24 hours, humanity wouldn’t even realize what had happened. But within days, the freshwater oceans would unleash their devastating effects.
First signs: Rising sea levels and unstable oceans
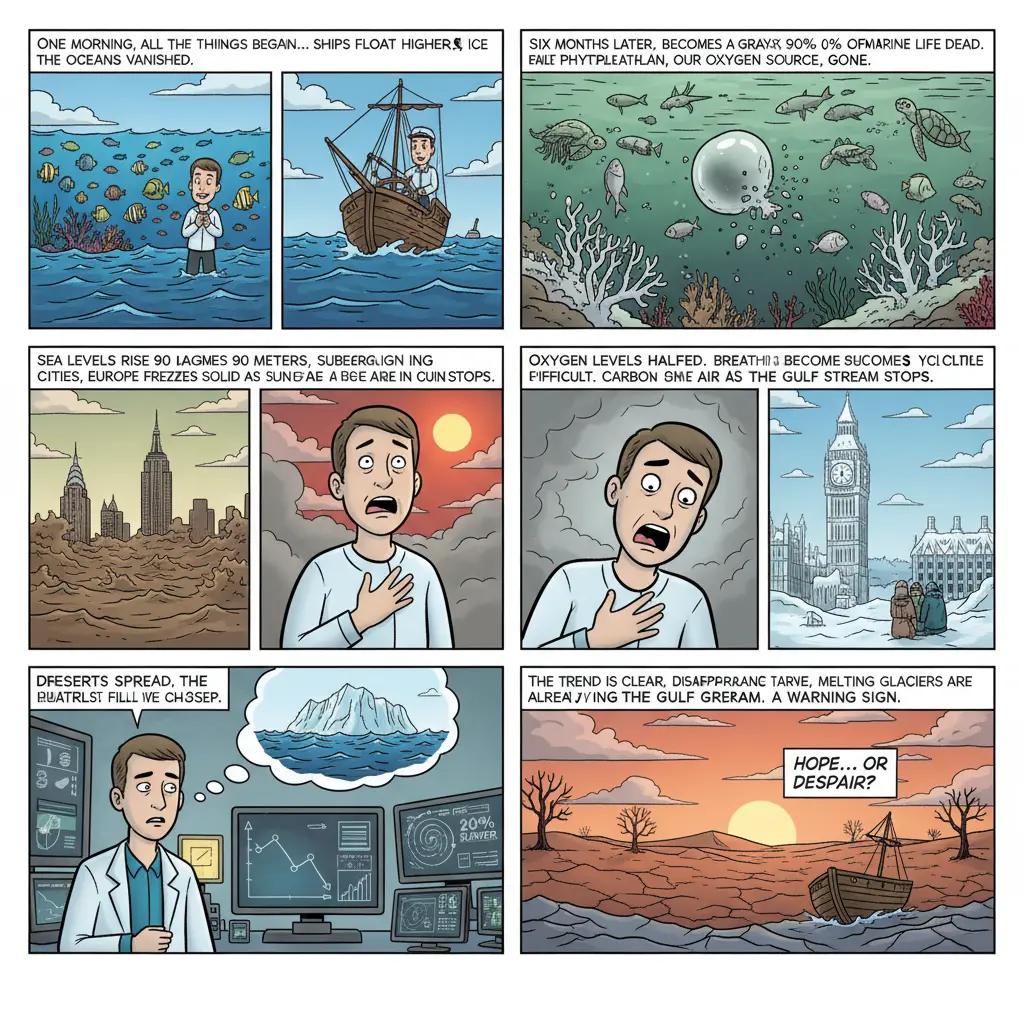
Seawater is only 2.6% denser than freshwater, so removing the salt would cause the ocean water to expand by that same percentage. This expansion alone would raise global sea levels by approximately 90 meters (300 feet), enough to submerge major coastal cities, including New York, London, Tokyo, the entire Netherlands, and Bangladesh etc.
Ships would float precariously higher, by about half a meter. The sudden rise in sea level would trigger massive tidal waves, reshaping coastlines worldwide.
Collapse of marine life and Earth’s oxygen supply
Within about 48 hours, the phytoplankton (microscopic algae) that produce over 50% of Earth’s oxygen would all die because they rely on salt to regulate their internal pressure. Without it, their cells would swell and burst. Within a week, half of the planet’s oxygen-producing system would be gone.
This loss would trigger a catastrophic chain reaction:
- Days 4–10: Zooplankton collapse
- Days 10–20: Small fish die
- Within a month: The oceans would be filled with billions of tons of rotting biomass
As oxygen levels in the water plummet, anaerobic bacteria would take over, rapidly producing methane and hydrogen sulfide. Vast areas of the ocean would become foul-smelling, suffocating reservoirs, with the stench reaching thousands of kilometers away.
Strange white gas bubbles (bio- geodesic domes) would rise from the depths. Within just six months, only extremophile bacteria and a few jellyfish species would survive. It would take millions of years for the marine ecosystem to recover.
The End of the Gulf Stream
One of the most serious consequences would be the shutdown of the Gulf Stream current, a vital ocean current that regulates weather in the Northern Hemisphere. This system relies on salty, dense water sinking and driving deep-ocean circulation.
If the oceans became freshwater, this density difference would disappear, and the Gulf Stream would stop. This would result in:
- London: Average annual temperature of approximately −30°C
- Paris: Siberian-like weather
- Oslo: Similar to Northern Greenland
This might sound like science fiction, but it’s not. Research has already shown that the Gulf Stream has slowed by 20% due to melting polar ice and reduced salinity in the North Atlantic.

Global Climate Extremes
Other regions would not be spared:
- Asia: Harsh winters and scorching summers exceeding 50°C (122°F)
- North America: Vast icy deserts
- Tropics: Extremely hot oceans, violent storms, and frequent tornadoes
Atmospheric and Ecosystem Collapse
The extinction of phytoplankton would lead to:
- Atmospheric oxygen levels dropping by up to 50%, making breathing difficult
- Carbon dioxide levels increasing, accelerating global warming
- The water cycle slowing by approximately 4%, enough to destabilize rainfall patterns.
Consequently, deserts would expand hundreds of kilometers northward, disrupting agriculture and freshwater availability.
Could this really happen?
Fortunately, it is virtually impossible for Earth’s oceans to turn into freshwater. Removing all the salt from the ocean would require a thousand times more energy than humanity produces annually. Only the sun could accomplish this – and not for at least a billion years, when its intensity will increase dramatically.
However, the warning signs are real:
- Glaciers are melting
- Ocean salinity is decreasing
- Major ocean currents are slowing down
Scientists agree that if these trends continue, the Earth could experience a smaller but still catastrophic version of this scenario.

About the Author
Manish is a Civil Servant. Users can follow Manish on Instagram ![]()
How the Nigerian boy lives now from the famous Photograph: Anja Ringgren Lovén
Since 2012, Anja Ringgren Lovén of Denmark has been the founder of a charitable organization…
6 thing to be remember if Travel to Spain
Travelling to Spain is an extremely thrilling experience. This country in Western Europe is surrounded…
Which is better for travelling in Indian trains AC II or AC III?
Whether to travel in AC-II (Second AC) or AC-III (Third AC) in Indian trains depends…
What 15 Common Items are Not Permitted in North Korea?
North Korea often pops up in our minds as a mysterious place with a secretive…
Shiny Dixit Biography: Journey of the Rising Star!
Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of Shiny Dixit, where laughter meets talent…
Why don’t I Dream anymore after Sleeping?
Having dreams means that you are in deep sleep and your mind is constantly weaving…






